
An Insecure Direct Object Reference (IDOR) vulnerability occurs when a web application exposes a reference to internal objects, such as files or database entries, without proper access control checks. This allows attackers to manipulate parameters in a URL to access unauthorized data.
A common example involves a file download URL:
https://insecure-website.com/
If the server doesn’t validate whether the requesting user is authorized to access that file, an attacker can simply change the file parameter to another file, such as: CV_Peter_Jones.pdf.
If successful, the attacker gains unauthorized access to Peter Jones' document, which may contain sensitive personal data.
Insecure Direct Object References (IDOR) occur when an application provides direct access to objects based on user-supplied input. As a result of this vulnerability attackers can bypass authorization and access resources in the system directly, for example database records or files.
Insecure Direct Object References allow attackers to bypass authorization and access resources directly by modifying the value of a parameter used to directly point to an object. Such resources can be database entries belonging to other users, files in the system, and more. This is caused by the fact that the application takes user supplied input and uses it to retrieve an object without performing sufficient authorization checks.
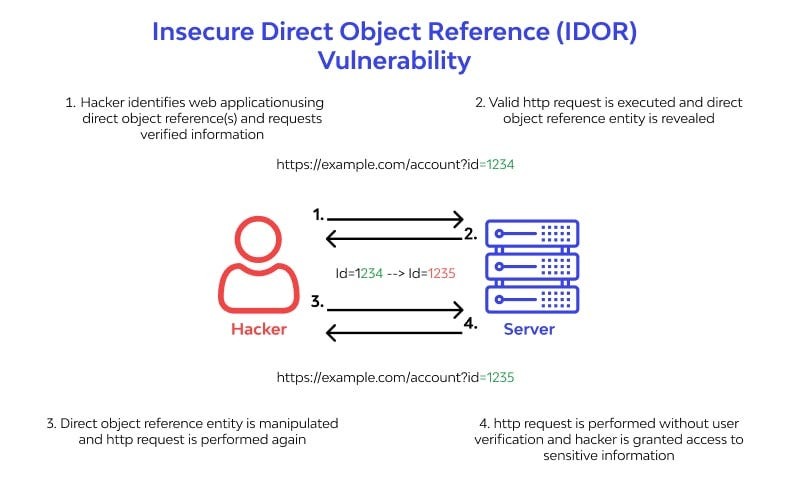
This vulnerability can also affect systems that use sequential identifiers in URLs. For instance:https://example.com/static/ can be changed to 2.pdf, 3.pdf, and so on — allowing an attacker to iterate through files and download them at will.
Another form appears in user info pages like https://example.com/, where increasing the ID might reveal another user's data if no access checks are in place.
Test Objectives
- Identify points where object references may occur.
- Assess the access control measures and if they’re vulnerable to IDOR.
How to Test
To test for this vulnerability the tester first needs to map out all locations in the application where user input is used to reference objects directly. For example, locations where user input is used to access a database row, a file, application pages and more. Next the tester should modify the value of the parameter used to reference objects and assess whether it is possible to retrieve objects belonging to other users or otherwise bypass authorization.
The best way to test for direct object references would be by having at least two (often more) users to cover different owned objects and functions. For example two users each having access to different objects (such as purchase information, private messages, etc.), and (if relevant) users with different privileges (for example administrator users) to see whether there are direct references to application functionality. By having multiple users the tester saves valuable testing time in guessing different object names as he can attempt to access objects that belong to the other user.
These scenarios highlight the critical importance of implementing strict server-side authorization checks to protect sensitive resources and prevent unauthorized access.
See What’s Next in Tech With the Fast Forward Newsletter
Tweets From @varindiamag
Nothing to see here - yet
When they Tweet, their Tweets will show up here.





























